Load data for caliber "9 mm Browning court"
The 9 mm Browning court is a rimless centerfire cartridge designed by John Browning in the late 1920s. It is based on his .38 ACP design, modified to use a 9mm-diameter projectile and bottlenecked case. This caliber is used in automatic pistols such as the Glock 17, Beretta 92FS, and Sig Sauer P226, and can also be fire-formed from .380 ACP brass.You find 9 mm Browning court with all common powders and bullets by clicking the 'Loads in this caliber' button above.
Technical Specifications (based on the respective safety standard - see more details in tab 'Datasheet' if available)
| Caliber: | 9 mm Browning court |
|---|---|
| Cartridge Type: | Pistol/Revolver |
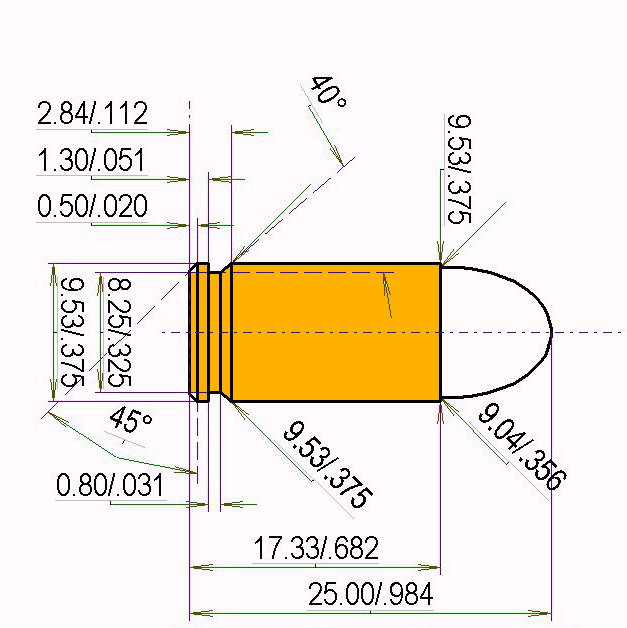
| Bullet Diameter: | 0.356 '' | 9.04 mm |
| Primer Size: | Small Pistol (SP) |
| Max. Case Length (l3): | 0.68'' | 17.3 mm |
| Max .Cartridge Length / OAL: | 0.98'' | 24.99 mm |
| Maximum Standardized Pressure: | 19580.4 psi | 1350 bar |

C.I.P.
The Commission internationale permanente pour l'épreuve des armes à feu portatives ("Permanent International Commission for the Proof of Small Arms" – commonly abbreviated as C.I.P.) is an international organisation which sets standards for safety testing of firearms. (The word portatives ("portable") in the name refers to the fact the C.I.P. tests small arms almost exclusively; it is ordinarily omitted from the English translation of the name.) As of 2015, its members are the national governments of 14 countries, of which 11 are European Union member states. The C.I.P. safeguards that all firearms and ammunition sold to civilian purchasers in member states are safe for the users.
To achieve this, all such firearms are first proof tested at C.I.P. accredited Proof Houses. The same applies for cartridges; at regular intervals, cartridges are tested against the C.I.P. pressure specifications at the ammunition manufacturing plants and at C.I.P. accredited Proof Houses.